|
||||||||||||||
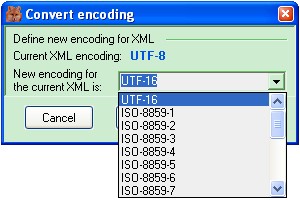
How to convert
XML encoding?
UTF-8... UTF-16...